Creating the Project
dotnet new globaljson --sdk-version 7.0.403 --output Chapter18
dotnet new web --no-https --output Chapter18 --framework net7.0
dotnet new sln -o Chapter18
dotnet sln Chapter18 add Chapter18
Nuget Packages
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design" Version="7.0.5">
</PackageReference>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SQLite" Version="7.0.5" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer" Version="7.0.5" />
Installing a Global Tool Package
dotnet tool uninstall --global dotnet-ef
dotnet tool install --global dotnet-ef --version 7.0.9
global.json version "version": "7.0.403"
Data Model consist 3 classes. Book, Publisher and Classification. Data Context :-
To create the Entity Framework Core context class that will provide access to the database, add a file called DataContext.cs to the Models folder.
public DataContext(DbContextOptions<DataContext> opts)
: base(opts) { }
public DbSet<Book> Books => Set<Book>();
public DbSet<Classification> Classifications => Set<Classification>();
public DbSet<Publisher> Publishers => Set<Publisher>();
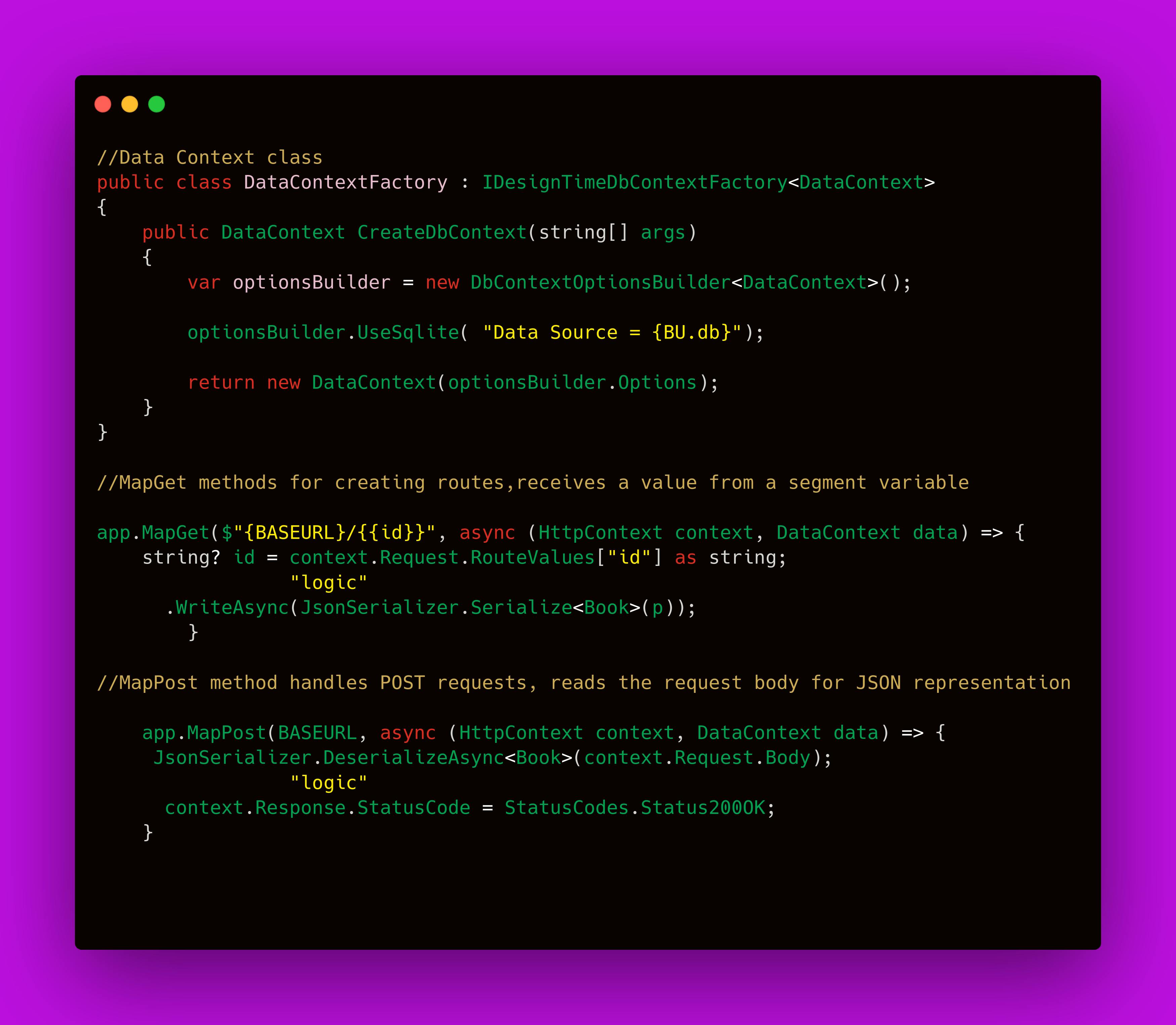
public class DataContextFactory : IDesignTimeDbContextFactory<DataContext>
{
public DataContext CreateDbContext(string[] args)
{
var optionsBuilder = new DbContextOptionsBuilder<DataContext>();
optionsBuilder.UseSqlite( "Data Source = {BU.db}");
return new DataContext(optionsBuilder.Options);
}
}
}
Connection String
builder.Services.AddDbContext<DataContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlite(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("BookConnection")));
Appsetting.json
"ConnectionStrings":{
"BookConnection": "Data Source=BU.db"
}
Migration
dotnet ef migrations add Initial
dotnet ef database update
Request Pipeline
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context, DataContext dataContext) {
if (context.Request.Path == "/test") {
await context.Response.WriteAsync(
$"There are {dataContext.Books.Count()} books\n");
await context.Response.WriteAsync(
$"There are {dataContext.Classifications.Count()} classifications\n");
await context.Response.WriteAsync(
$"There are {dataContext.Publishers.Count()} publishers\n");
} else {
await nextDelegate(context);
}
}
web service defines an API through a combination of URLs and HTTP methods such as GET and POST, which are also known as the HTTP verbs. The method specifies the type of operation, while the URL specifies the data object or objects that the operation applies to.
Most RESTful web services format the response data using the JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) format.
| HTTP METHOD | DESCRIPTION | |
| GET | retrieve one or more object | |
| POST | create a new object | |
| PUT | update an existing object | |
| PATCH | update part of an existing object | |
| DELETE | delete an object |
Creating a Web Service using Minimal API
The MapGet and MapPost methods are used to create routes, all of which match URLs that start with /api, which is the conventional prefix for web services.
app.MapGet($"{BASEURL}/{{id}}", async (HttpContext context, DataContext data) => {
string? id = context.Request.RouteValues["id"] as string;
`logic`
.WriteAsync(JsonSerializer.Serialize<Book>(p));
}
}
The endpoint for the first route receives a value from a segment variable that is used to locate a single Book object in the database.The endpoint for the first route receives a value from a segment variable that is used to locate a single Book object in the database.
app.MapGet(BASEURL, async (HttpContext context, DataContext data) => {
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json";
await context.Response.WriteAsync(JsonSerializer
.Serialize<IEnumerable<Book>>(data.Books));
});
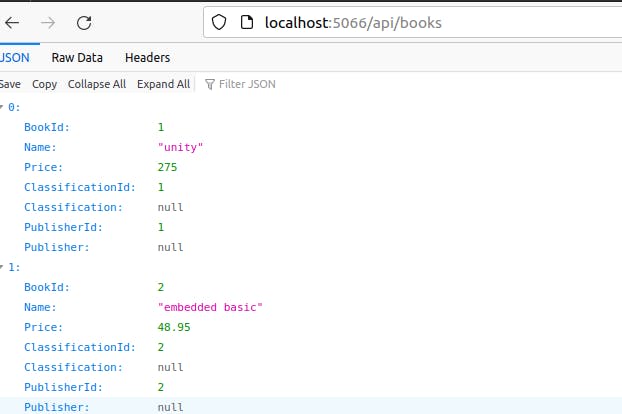
This endpoint retrieves all the Book objects in the database.
app.MapPost(BASEURL, async (HttpContext context, DataContext data) => {
Book? p = await
JsonSerializer.DeserializeAsync<Book>(context.Request.Body);
if (p != null) {
await data.AddAsync(p);
await data.SaveChangesAsync();
context.Response.StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status200OK;
}
The third endpoint handles POST requests and reads the request body to get a JSON representation of a new object to add to the database.